How to check if your hard drive is detected by computer BIOS/CMOS
One of the major computer diagnostic tools for PC computer is BIOS / CMOS screen. There is a standard procedure to gain the access to BIOS screen (an example on picture below). Turn off and on the computer for a cold reboot, when reboot immediately start keying [DELETE] button on your keyboard. Some PC computers have different 'escape to BIOS' keys, so you should refer to your computer’s manual if the [DELETE] button is not working.
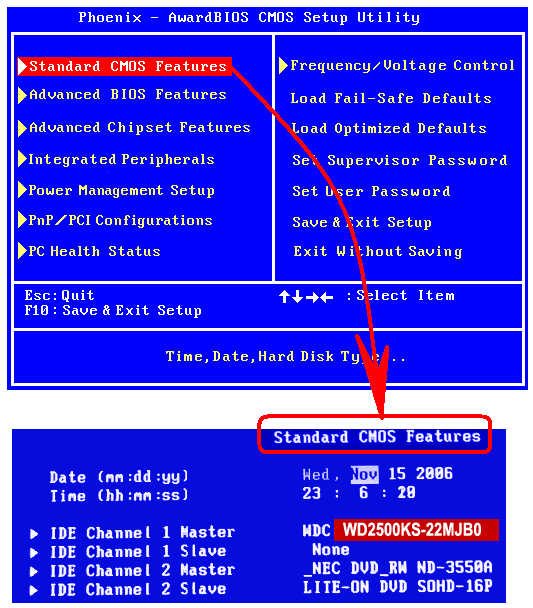
Once you are in BIOS, browse its menu to check if your hard drive is there (recognized).
On the illustrated example above, BIOS recognized a 250 GB Western Digital hard drive, the model number is WD2500KS, write it down to check if the same number is demonstrated on the label of your hard disk drive.
Now, you may turn off the computer, unplug all cables, open the system box, and remove the hard drive from the machine.

Compare BIOS model number to the number on your hard drive label. If these numbers are different, you have a problem with the hard drive.
If the drive is failed in BIOS, or shows the different model number, there is no doubt you need to seek for a professional data recovery service.
If the drive is showing the real model number, you may try to connect this drive to the different machine. The best way to do it is using an external USB enclosure.
There is no guarantee, that the passed BIOS test hard drive will start working and you can access your data.
There still maybe many issues, when the drive is in need for an evaluation at professional data recovery service.
If you connect the suspicious drive to other computer and still cannot access the data:
Under no circumstances should you continue using the device as you may cause further damage to the unit. Also, you should not allow the system to run a repair utility on the drive (such as Scandisk / Chkdsk / Norton etc) - this can often render yet recoverable data to its permanent loss.